| Contents | |
|---|---|
 Impenetrable Cryptography
Impenetrable Cryptography
|
A World-First in cryptography. |
 Cryptographic Features
Cryptographic Features
|
New and unique cryptographic properties |
 Summary
Summary
|
The fractal transformation security revolution |
Impenetrable Cryptography
Fractal Transformation is an innovative encryption technology that offers quantum impenetrability.
Classic cryptography teaches that 'all encryption is crackable', essentially meaning that all classic block encryption can be brute-force decrypted (trying every possible key). This was true as only the correct key would return a sensible result.
AES was considered secure because of the large number (2 ^ 256) of possible combinations that would take classic computers a very long time to brute-force. Quantum computers have the amazing capacity to 'see' all combinations at once, undermining AES security.
Fractal Transformation is considered impenetrable due to multiple unique properties.
Cryptographic Features
Fractal Transformation is a new cryptographic art and science that is unrelated to classic block encryption.
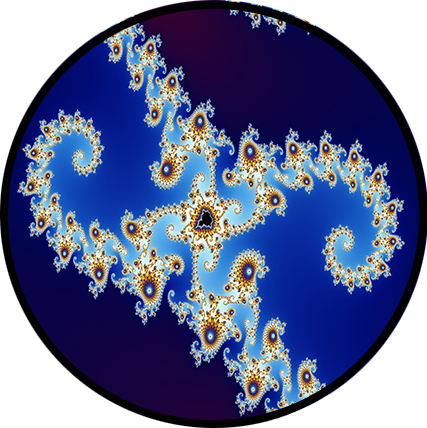
Fractal Transformation engineers the awesome Mandelbrot Fractal, proven to be infinitely complex, to securely encrypt data, keys, communication etc in such a manner as to make it Guaranteed Quantum Proof.
It is a World-First impenetrable encryption technology.
It has unique and novel properties, including:
1. Infinite Key Space
Fractal Transformation’s key space is based on the infinite complexity of the Mandelbrot set that is proven to be infinitely complex.
The infinite key space allows for unlimited key generation, with each key linked to a unique and complex fractal mapping. This results in an unbounded number of possible keys.

There is no upper limit to Fractal Transformation key space; it can be increased arbitrarily.
2. Configurable Key Space
Fractal Transformation’s key space precision is configurable by way of Multi-Dimensional Mandelbrot Fractals where each dimension ads 112 bits. There is no theoretical limit to the number of dimensions and key space bits. Practical limits are processor and RAM based.
Our Fractal Encryption Standard has been tested beyond 40,000 dimensions that equals a 4,480,000 bit key space.
3. Key Non-Determinism
In Fractal Transformation, the key does not directly affect the payload. The transformation is independent of the key shape once the fractal portal is identified via the above key space.
This property eliminates the ability to predict or reverse the transformation based on the key shape. There is no determinism in how the key relates to the transformation after the portal is discovered.
Unlike block encryption where the key directly acts on the payload, in Fractal Transformation, the key only serves to navigate to the fractal portal. The transformation process that follows is driven entirely by fractal dynamics, making it impossible to reverse-engineer or discover the key based on the ciphertext.
4. Indistinguishability of Ciphertexts
With Fractal Transformation, a ciphertext can result in innumerable plausible plaintexts when decrypted with different keys.
This leads to the indistinguishability of ciphertexts, making it impossible for an attacker to discern which decryption result is the correct one.
The vast number of possible decryptions from even a single ciphertext creates an environment where random, semi-sensible, and sensible plaintexts all appear as viable outputs. No external method can determine which output is the original. This means that a brute-force attempt is not feasible.
5. Complexity of Fractal Navigation
The process of navigating the Mandelbrot set to generate the Fractal Stream is inherently complex and unpredictable.
The infinite pathways through fractal space ensure that an attacker cannot anticipate or reverse the encryption process.
Fractal Transformation navigation from point to point in the Mandelbrot set is non-linear, with each new point dependent on previous complex values and portal locations. This recursive, unpredictable navigation guarantees computational infeasibility for adversaries.
6. Fractal Stream complexity is significantly greater than any Key
Importantly, the Complexity of Fractal Stream generated significantly exceeds the complexity and unpredictability of any key, matching the size of the payload.
Fractal Transformation does not rely on the complexity and unpredictable quality of the key to deliver infinite complexity and unpredictability during encryption.
The key acts to identify a fractal portal (see key space above), from there the Infinite Complexity of Fractal Navigation generates a fractal stream, transforming and encrypting without further reference to the key.
7. Quantum Impenetrability
Fractal Transformation is impenetrable by quantum-based attacks, including those leveraging Flatow’s algorithm.
The infinite key space and the impossibility of distinguishing between sensible decryption results, combined with the non-linear transformation, ensure that no quantum algorithm can effectively brute-force or reverse-engineer the fractal stream.
Flatow’s Algorithm theoretically shows the capability of brute-forcing classic block encryption with 400 qubits; however, the infinite complexity of the fractal key space, along with the inability to discern correct results, closes the door on any computational means of penetrating Fractal Transformation, now or in the future.
Summary
The combined effect of these properties ensures that Fractal Transformation is impenetrable by any known computational means, both classical and quantum.
This demonstrates that Fractal Transformation offers a secure foundation for encryption in the post-quantum era, providing a robust defense against current and emerging threats posed by quantum computing.